Introduction:
In today's health-conscious world, water purifiers have become an integral part of households, ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water. While their efficacy in removing contaminants is widely acknowledged, concerns about electricity consumption often arise.
Types of Water Purifiers and Electricity Consumption
Gravity-Based Water Purifiers: Gravity-based purifiers do not require electricity as they rely on the force of gravity to pass water through filtration media. These are the most energy-efficient options, making them ideal for areas with erratic power supply or off-grid locations.
UV Water Purifiers:UV purifiers use ultraviolet light to disinfect water and eliminate harmful microorganisms. They have a low electricity consumption as the UV lamp requires minimal power to operate. On average, a UV water purifier consumes around 30 to 40 watts per hour.
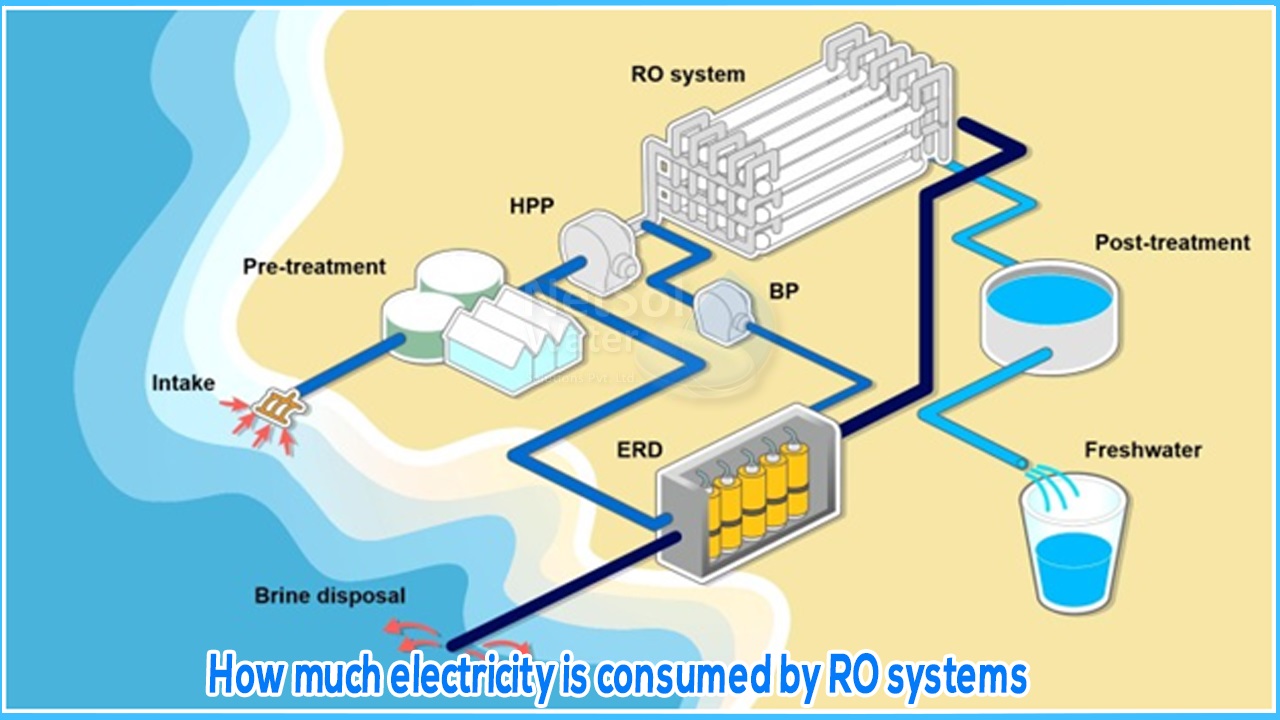
RO (Reverse Osmosis) Water Purifiers: RO purifiers use a pump to force water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing impurities and contaminants. The electricity consumption of RO purifiers is higher compared to UV purifiers due to the pump's operation. Typically, an RO water purifier consumes around 60 to 120 watts per hour.
UF (Ultrafiltration) Water Purifiers: UF purifiers work without electricity, relying on a gravity-based system or water pressure to pass water through the UF membrane. Consequently, they consume zero electricity during the filtration process.
RO+UV Water Purifiers: RO+UV purifiers combine the benefits of both RO and UV technologies, which leads to a higher electricity consumption than individual RO or UV purifiers. The average electricity consumption for RO+UV purifiers ranges from 90 to 150 watts per hour.
Factors Affecting Electricity Consumption
Several factors influence the electricity consumption of water purifiers:
a. Daily Usage: The frequency and duration for which the water purifier is operational each day directly impact its electricity consumption. Purifiers used more frequently will consume more power.
b. Water Pressure: In RO and UF purifiers, the water pressure affects the efficiency of the filtration process. Lower water pressure may require the pump to work harder, increasing electricity usage.
c. Capacity: The capacity of the water purifier's storage tank also influences electricity consumption. Larger storage tanks may require the pump to run more frequently to fill the tank, resulting in higher energy consumption.
d. Purifier Condition: Regular maintenance and timely replacement of filters ensure the purifier operates optimally, reducing the strain on its components and electricity consumption.
Tips to Optimize Electricity Usage
To reduce electricity consumption without compromising water quality, consider the following tips:
a. Choose the Right Type: Select a water purifier that aligns with your water quality and usage requirements. For areas with a reliable water supply, a gravity-based or UV purifier might suffice.
b. Opt for Energy-Efficient Models: Look for water purifiers with energy-saving features and high star ratings, indicating better energy efficiency.
c. Regular Maintenance: Ensure timely maintenance and filter replacements to keep the purifier running efficiently, reducing energy wastage.
d. Turn Off UV Lamp When Not Needed: If your UV purifier has a manual switch for the UV lamp, turn it off when purifying water that doesn't require disinfection.
Conclusion:
The electricity consumption of a water purifier varies depending on its type, daily usage, capacity, and maintenance. While some purifiers consume minimal electricity like gravity-based and UF purifiers, others like RO and RO+UV purifiers may have higher consumption due to the pump's operation. By selecting the right purifier for your needs and implementing energy-saving practices, you can strike a balance between having access to clean water and managing electricity consumption responsibly. Ultimately, investing in a water purifier remains a vital step towards ensuring the health and well-being of your family.