Water is a vital resource that we rely on for various purposes, including drinking, cooking, and cleaning. However, the quality of water available to us is not always up to the desired standards. To address this issue, various water purification methods have been developed, and one of the most effective ones is Reverse Osmosis (RO). RO water purification systems use a multi-stage process to remove impurities and provide us with clean and safe drinking water. In this article, we will explore the different stages of RO water purification and understand how they work to deliver high-quality drinking water.
Stage 1: Pre-filtration
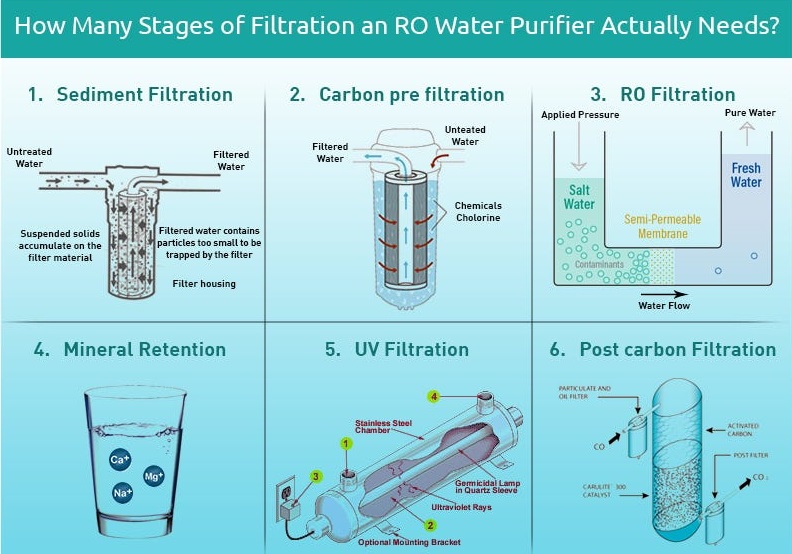
The first stage of the RO water purification process involves pre-filtration. This stage typically consists of a sediment filter or a pre-filter, which removes larger particles such as sand, dirt, rust, and sediment from the water. These particles can clog the RO membrane, so the pre-filter helps prolong the life of the membrane and improves the overall efficiency of the system.
Stage 2: Carbon Filtration
In the second stage, the water passes through a carbon filter. This filter contains activated carbon, which helps remove chlorine, chloramines, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other chemicals that affect the taste, odor, and overall quality of the water. The carbon filter also helps protect the RO membrane from damage caused by chlorine.
Stage 3: Reverse Osmosis
The third stage is the heart of the RO water purification process. Here, water is forced through a semipermeable membrane under high pressure. The RO membrane has extremely tiny pores that allow water molecules to pass through while blocking larger contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, dissolved solids, and other impurities. This process effectively removes up to 99% of the contaminants present in the water, ensuring its purity.
Stage 4: Post-filtration
After the water has passed through the RO membrane, it goes through a post-filter, also known as a polishing filter. This filter helps further improve the taste and quality of the purified water by removing any residual tastes or odors. It ensures that the water delivered to the faucet is clean, clear, and free from any remaining impurities.
Stage 5: Storage and Delivery
Once the water has gone through the purification stages, it is stored in a pressurized storage tank. This tank holds the purified water until it is needed, ensuring a constant supply of clean water. When you turn on the faucet, the purified water flows out and is ready for use.
Conclusion:
Understanding the different stages of RO water purification helps us appreciate the complexity of the process and the effectiveness of RO systems in providing clean drinking water. The combination of pre-filtration, carbon filtration, reverse osmosis, and post-filtration ensures the removal of a wide range of impurities, making the water safe and healthy for consumption. RO water purification systems have become increasingly popular due to their ability to deliver high-quality water, contributing to the well-being of individuals and communities worldwide.